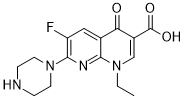
Chemical Structure : Enoxacin
CAS No.:
74011-58-8
Enoxacin
(AT-2266, CI-919)
Catalog No.: PC-23990Not For Human Use, Lab Use Only.
Enoxacin (Enoxacin sesquihydrate) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, interferes with DNA replication and inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase (IC50=126 µg/ml) and topoisomerase IV (IC50=26.5 µg/ml).
Enoxacin is a miRNA processing activator and enhances siRNA-mediated mRNA degradation and promotes the biogenesis of endogenous miRNAs.
Enoxacin shows potent activities against gram-positive and -negative bacteria.
Enoxacin is a cancer-specific growth inhibitor that acts by enhancing TAR RNA-bi
Bulk size, bulk discount!
Welcome credit card payment!
E-mail: sales@probechem.com
Tech Support: tech@probechem.com
Purity & Documentation Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Biological Activity
Enoxacin (Enoxacin sesquihydrate) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, interferes with DNA replication and inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase (IC50=126 µg/ml) and topoisomerase IV (IC50=26.5 µg/ml).
Enoxacin is a miRNA processing activator and enhances siRNA-mediated mRNA degradation and promotes the biogenesis of endogenous miRNAs.
Enoxacin shows potent activities against gram-positive and -negative bacteria.
Enoxacin is a cancer-specific growth inhibitor that acts by enhancing TAR RNA-binding protein 2 (TRBP)-mediated microRNA processing.
Physicochemical Properties
|
M.Wt
|
320.32
|
|
Formula
|
C15H17FN4O3
|
|
Appearance
|
Solid
|
|
CAS No.
|
|
|
Storage
|
- Solide Powder
-
-20°C 12 Months; 4°C 6 Months
|
- In Solvent
-
-80°C 6 Months; -20°C 6 Months
|
|
Shipping
|
|
|
Solubility
|
10 mM in DMSO
|
|
Chemical Name/SMILES
|
1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid
|
References
1. Ge Shan, et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2008 Aug;26(8):933-40.
2. Sonia Melo, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 15;108(11):4394-9.
3. M Takei, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Dec;45(12):3544-7.
Contact Us
sales@probechem.com